The world of broadband is often confusing for those not in the industry so we’ve provided a list of the most common acronyms and broken down some technical jargon to help you out.
Whether you want to know more before upgrading your broadband or simply want to understand how your internet connection works, this glossary should make things a little less confusing.
ADSL/ADSL2+ (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line): This allows for fast transfer of data across telephone lines, running both a telephone and broadband connection at the same time. Although an ADSL line will allow minimum speeds of 8Mb, the ADSL2+ is now found at most exchanges in the UK for speeds averaging 10-11Mb.
Asymmetrical broadband: This refers to an internet connection that either has a faster upload or download speed. Normally, the download speed is prioritised for domestic properties, which means upload speeds are usually slower.
Bandwidth: This refers to how capable your internet connection is at transferring data. Certain internet activity uses more bandwidth such as high-definition video streaming which often means other activities will slow down. If you upgrade to ultrafast full fibre broadband this problem should be alleviated.
Direct Bury: This term is in relation to a Direct-Buried Cable (DBC), an electrical cable buried under the ground without protection from sheathing or piping.
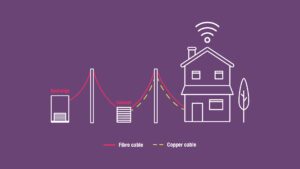
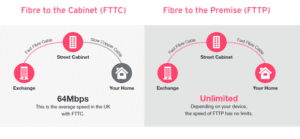
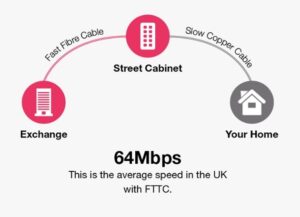
FTTC (fibre to the cabinet): This type of fibre broadband is delivered over fibre optic cables, but will end at the cabinet. The copper wire then carries the signal from the cabinet to your home.
FTTP (fibre to the premises) and FTTH (fibre to the home): This involves a fibre optic cable running from a cabinet, a green metal box you may have seen in your area, straight to your house.
FTTx (fibre to the x): A collective term for fibre infrastructure, or any broadband network that uses a physical fibre link.
Gbps (gigabits per second): In terms of broadband, this is used as a measurement for fast broadband speeds. There are 1000 megabytes (refer below) in a gigabyte.
IP address: An internet protocol address is made up of a collection of numbers and acts as the identifier for every device that connects to the internet.
ISP (internet service provider): A company that provides internet services and packages to homes and businesses
LAN (local area network): This refers to a group of devices in one set location, usually in a home or office, which allows multiple devices to connect with each other.
Latency: This is the reactive speed of your internet connection, the amount of time it takes to send data and receive a reply. It’s measured in milliseconds (ms). If this speed is too high, it can create what’s called “lag” and can affect things like streaming and gaming.
Mbps (megabits per second): This is another measurement of speeds and the one used most when we talk about broadband. One megabyte is equal to one million or, more accurately, 1,048,576 bytes.
SDSL (Symmetrical Digital Subscriber Line): This subscriber line allows the same speed for both uploads and downloads and is currently mostly used by businesses.
Superfast broadband: Refers to broadband speeds between 30-300Mbps.
Symmetrical broadband: An internet connection that has the same download and upload speed.
Ultrafast broadband: Refers to broadband speeds of more than 300Mbps.
VPN (virtual private network): This is a means to keep your digital data secure. A VPN hides your IP address by directing your internet activity through another server. It can also make your internet connection more secure, protecting your privacy online.
Wi-Fi (wireless technology): This acronym refers to the radio waves that allow mobile devices to access the internet wirelessly.
WAN (wide area network): This allows networks to be spread over large geographic areas. A WAN is normally used by large companies,
institutions, and government facilities.